Soyuz Spacecraft: Backbone of Russian Space Program

The Soyuz is a type of spacecraft that the Soviet Union, and then Russia, has used for decades to launch cosmonauts into space. Today's Soyuz missions are best known for trips to the International Space Station; however, the spacecraft has a long operational history dating back to the 1960s, starting with its first uncrewed mission on Nov. 28, 1966. Over the years, Soyuz spacecraft have sent cosmonauts to several types of space stations — the Almaz series, Salyut series, Mir and today's ISS.
Soyuz had two fatal missions. In 1967, the first crewed Soyuz mission, Soyuz 1, ended in tragedy due to a parachute failure that killed its sole cosmonaut, Vladimir Komarov. The first three-person Soyuz, Soyuz 11, in 1971, also had fatal consequences for its three crewmembers (who weren't wearing full spacesuits) after the cabin lost pressure shortly before re-entry.
For years, the only method of delivering crew to the ISS was the Soyuz craft, leading NASA to purchase seats for their astronauts. According to Spaceflight Now, NASA bought 71 seats at a cost of nearly $4 billion over the course of six years. As of 2020, the SpaceX Dragon rockets can deliver American crew to the space station.
Soyuz spacecraft are launched atop Soyuz rockets, a line of Russian boosters that have seen variants fly since the mid-1960s.
Design elements
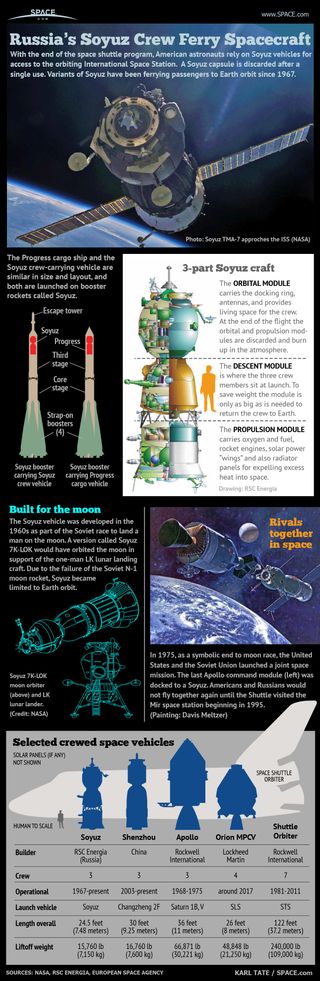
Soyuz is a single-use spacecraft designed to carry three inhabitants for several weeks, although today most crews use them for just a few hours or days in between six-month stays at the space station. The spacecraft includes an orbital module for missions; a re-entry module to come back to Earth; and a service module that has engines, instruments and other necessities to run the mission. Crews breathe an oxygen/nitrogen mixture that is at partial atmospheric pressure compared to Earth.
Soyuz has gone through about 10 variants since the 1960s. The most recent variants include Soyuz-TM, used for missions to the Mir space station, and three versions used for the ISS: Soyuz-TMA (retired in 2012), Soyuz TMA-M (retired in 2016) and Soyuz MS (in service since 2016). The current version, Soyuz MS, has a height of 24.5 feet (7.48 meters) and a maximum diameter of 9 feet (2.7 m), according to manufacturer RKK Energia. The solar panels extending from the module span 35 feet (10.7 m).
Notably, the Chinese Shenzhou crewed spacecraft uses the same technology as the Soyuz TM, although the spacecraft is not directly related to the Soyuz line, according to The Guardian. Russian cargo spacecraft called Progress, which are used to service the ISS, are also derived from the Soyuz.
Brief launch history
The first few spacecraft missions were Soyuz 1 through Soyuz 11 (1967-1971). While this generation encompassed several Soyuz spacecraft types, they tend to be grouped into one generation because they used bent solar panels (unlike future generations of Soyuz) and also had an automatic docking navigation system. Of note, Soyuz 11 docked to Salyut 1, the first Soviet space station. The Soviet Union also designed a variant (Soyuz 7K-L1) to bring cosmonauts around the moon; the design was tested with several uncrewed Zond missions that collected data on nearby celestial bodies such as the moon.
The second generation of Soyuz was used for Soyuz 12 through Soyuz 40 (1973-1981), according to Aerospace Technology. Cosmonauts in these spacecraft docked with the Almaz (military) and Salyut (civilian) space stations. This generation also included the Soyuz 7K-TM spacecraft, which docked with a U.S. Apollo spacecraft during the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975.
The third-generation Soyuz-T (1976-1986) had solar panels that gave the opportunity for longer missions, according to Aerospace Technology. These missions commonly visited the Salyut series of space stations. Notably, Soyuz T-10a was supposed to visit the Salyut 7 space station in 1983, but the launch escape system fired and saved the crew from a launch vehicle explosion.
The fourth generation of Soyuz vehicles were used to visit Mir (in the case of Soyuz-TM) and the International Space Station (for Soyuz-TM, Soyuz-TMA and Soyuz-TMA-M and Soyuz MS), according to Aerospace Technology. The latest version, Soyuz MS, includes changes such as more efficient solar panels, a more fuel-friendly approach and docking system and a new computer. The Soyuz MS-02 spacecraft made its first flight on Oct. 19, 2016, with the Expedition 49 crew on board.
Future
Now that the SpaceX Crew Dragon rockets are available to deliver NASA astronauts to the ISS, NASA is unlikely to purchase more seats aboard the Soyuz vehicles. But as of early 2021, there is no indication that Russian cosmonauts will stop using the craft.
The ISS is expected to cease operations around 2024 or 2025, as the Trump administration has requested no funding for the orbiting complex in 2025. Currently, the international partners in the space station agreement are discussing a new lunar space station called the Deep Space Gateway. This would send astronauts (and possibly Russian cosmonauts) to missions near the moon, providing practice for longer-term missions to Mars and other locations in the solar system.
This article was updated on Jan. 26, 2021 by Space.com Reference Editor Vicky Stein.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
